The Unlikely Journey of C15 Fatty Acid
The Unlikely Journey of C15 Fatty Acid
Science surprises us. From studying dolphins to revolutionizing human nutrition, the story of C15 fatty acid reveals how scientific curiosity transforms our understanding of essential nutrients. What began as marine mammal research has evolved into a critical chapter in nutritional science that challenges conventional wisdom about fat consumption.
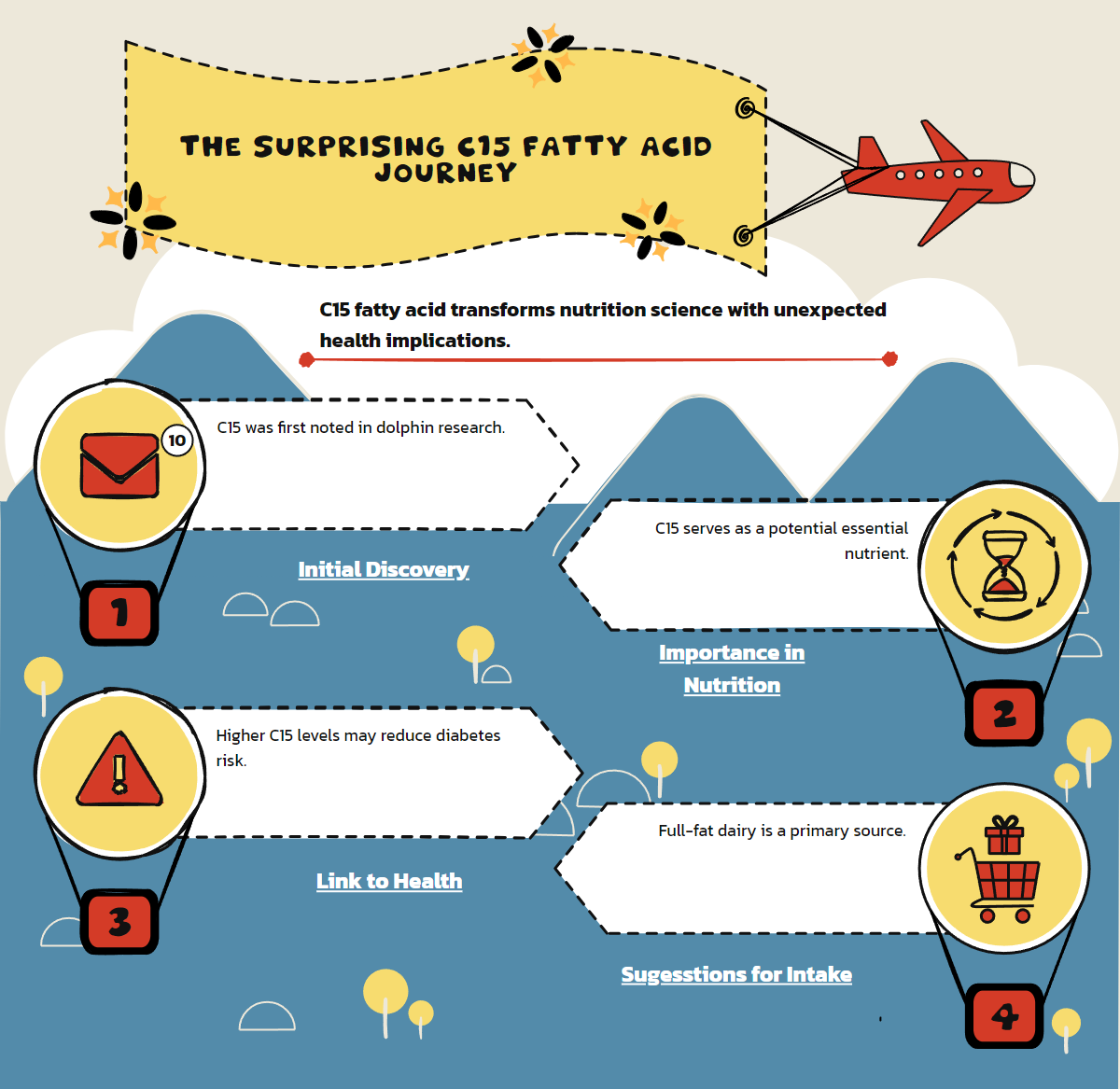
The discovery of pentadecanoic acid (C15) represents one of those quiet scientific revolutions that reshape our understanding without fanfare. This odd-chain saturated fatty acid first caught researchers' attention during studies of dolphin metabolism in the 1970s. Scientists noted its unusual presence and stability across marine mammal populations but initially considered it merely a biological curiosity.
From Marine Mammals to Human Health
For decades, C15 remained in scientific obscurity. While researchers documented its presence in dairy products and some fish, nutrition science focused almost exclusively on more abundant fatty acids. The prevailing nutritional paradigm categorized saturated fats as universally harmful, leaving little room for nuanced investigation of individual fatty acid properties.
This changed when epidemiological studies began revealing unexpected correlations. People with higher circulating levels of C15 showed lower rates of metabolic disorders. The scientific community took notice. Could this overlooked molecule play a more significant role than previously thought?
Subsequent research confirmed that C15 serves as a reliable biomarker for dairy fat consumption. Unlike many nutrients that fluctuate widely in the bloodstream, C15 levels remain remarkably stable, making it an ideal indicator of long-term dietary patterns. This discovery opened new avenues for nutrition research, allowing scientists to more accurately track relationships between specific foods and health outcomes.
Rewriting Nutritional Understanding
The most fascinating aspect of C15 research lies in how it challenges established nutritional dogma. Multiple large-scale studies have now linked higher C15 levels with reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, improved insulin sensitivity, and better cardiovascular outcomes. These findings directly contradict the simplistic view that all saturated fats negatively impact health.
Researchers now recognize that C15 appears to function as a cellular signaling molecule, influencing how our cells process energy and respond to metabolic stress. Its odd-chain structure gives it unique properties compared to even-chain saturated fats, allowing it to integrate into cell membranes and modify their function in ways that promote metabolic resilience.
What makes this story particularly compelling is how it illustrates the danger of nutritional oversimplification. By lumping all saturated fats together, scientists nearly missed the unique benefits of this specific fatty acid. The C15 story serves as a powerful reminder that nutritional science requires nuance and precision.
Beyond Biomarkers
Recent research has elevated C15 from mere biomarker to potential essential nutrient. Studies suggest that adequate C15 intake may help regulate mitochondrial function, reduce cellular inflammation, and promote metabolic flexibility. These properties make it particularly relevant to addressing modern metabolic challenges like insulin resistance and obesity.
The primary dietary sources of C15 include full-fat dairy products, certain fish, and some plant oils. Interestingly, grass-fed dairy contains significantly higher concentrations than conventional dairy, highlighting how agricultural practices influence nutritional composition. This connection between food production methods and nutritional quality adds another layer to the already complex relationship between diet and health.
Nutritional scientists now face the challenge of determining optimal C15 intake levels. Unlike macronutrients with established dietary guidelines, trace nutrients like C15 require more nuanced recommendations that account for individual metabolic differences and dietary patterns.
Future Nutritional Frontiers
The evolving understanding of C15 points to broader shifts in nutritional science. We're moving from broad categorical recommendations toward precision nutrition that recognizes the complex interplay between specific compounds and individual physiology. This transition requires both advanced research techniques and a willingness to question established nutritional paradigms.
For consumers, the C15 story offers a valuable lesson in nutritional humility. Today's nutritional villain may be tomorrow's essential nutrient. Rather than following categorical food rules, building dietary patterns around minimally processed foods that have sustained human health throughout evolutionary history likely provides the most reliable path to nutritional adequacy.
Researchers continue exploring potential therapeutic applications for C15 supplementation, particularly for metabolic disorders. Early investigations suggest promising effects on insulin sensitivity and inflammatory markers, though clinical applications remain in early development stages.
From Obscurity to Essential
The journey of C15 fatty acid from obscure marine mammal research to potential essential nutrient status exemplifies how scientific understanding evolves. What began as a curious observation in dolphin metabolism has developed into a significant area of nutritional research with implications for dietary recommendations and metabolic health.
This scientific journey reminds us that nutrition science constantly evolves. The most valuable approach combines evidence-based recommendations with openness to new discoveries. The C15 story isn't just about one fatty acid but about the iterative nature of scientific progress and the importance of questioning even our most established nutritional beliefs.
As research continues, C15 may earn formal recognition as an essential nutrient. Regardless of its ultimate classification, its story has already enriched our understanding of how specific dietary components influence health. From dolphins to dairy to diabetes prevention, this unlikely nutritional journey continues unfolding, one research study at a time.