The Hidden Healing Power of Your Own Stem Cells
The Hidden Healing Power of Your Own Stem Cells
What if the most powerful regenerative medicine was already circulating through your bloodstream?
While stem cell therapies often conjure images of expensive injections and complex procedures, a quieter revolution has unfolded in regenerative medicine. Scientists have discovered that certain natural compounds can stimulate your body to release its healing stem cells, potentially transforming how we approach tissue repair and regeneration.
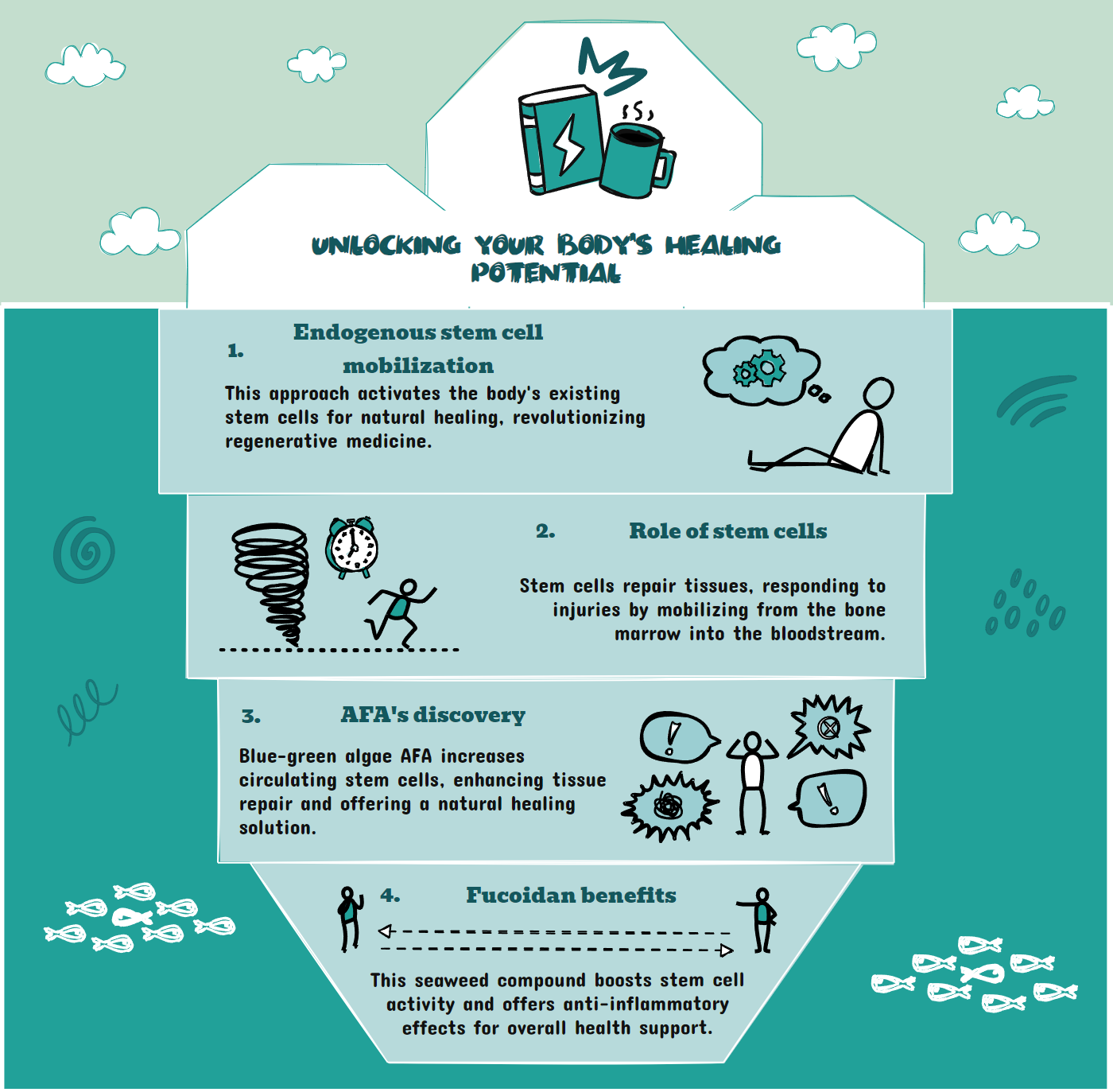
This approach, known as endogenous stem cell mobilization, represents a fundamental shift in regenerative medicine. Rather than introducing external stem cells, it focuses on activating the vast reservoir of healing cells in the body.
Your Body's Built-in Repair System
Stem cells function as the body's natural repair system, constantly monitoring for damage and responding to injuries. When injured, tissues emit chemical signals that trigger a cascade of healing events.
These signals prompt bone marrow to release stem cells into the bloodstream. The mobilized cells then migrate to damaged areas, where they can differentiate into the specific cell types needed for repair.
This natural process occurs continuously throughout life, though its efficiency diminishes with age. By age 30-40, the body's stem cell production and mobilization capacity have typically declined significantly as red bone marrow gradually converts to yellow marrow.
More stem cells in circulation have been linked to greater health, while fewer circulating stem cells correlate with disease formation—a finding with profound implications for regenerative medicine and anti-aging approaches. This connection between circulating stem cells and health has opened new avenues for preventive medicine.
The Blue-Green Algae Discovery
Neurophysiologist Christian Drapeau's work significantly advanced the science of natural stem cell mobilization. His research focused on a blue-green algae from Klamath Lake called Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (AFA).
Drapeau discovered that AFA works by stimulating stem cell mobilization from the bone marrow, increasing the number of circulating stem cells available to participate in tissue repair and renewal. This finding revolutionized our understanding of how natural compounds might influence the body's regenerative capabilities.
The evidence is compelling. A double-blind randomized crossover study found that consuming AFA extract increased the number of circulating stem cells by approximately 25%. The research confirmed that AFA contains an L-selectin ligand that stimulates stem cell release from bone marrow, providing scientific validation for this natural approach to stem cell activation.
The Power of Seaweed Compounds
Another remarkable natural stem cell mobilizer comes from the sea. Fucoidan, a complex polysaccharide found in various species of brown seaweed, has demonstrated significant effects on stem cell activity.
Research has shown that Fucoidan has anti-inflammatory properties and increases the baseline number of circulating stem cells over time. This sustained elevation in stem cell levels may explain the traditional use of seaweed in many longevity-focused diets worldwide.
Fucoidan is particularly valuable because it works through different mechanisms than AFA, potentially offering complementary benefits when the compounds are used together.
How Natural Stem Cell Mobilizers Work
The mechanism behind these natural compounds is elegant in its simplicity. AFA and Fucoidan interact with specific receptors in the bone marrow that control stem cell release.
AFA contains compounds that bind to L-selectin, a cell adhesion molecule that plays a crucial role in stem cell mobilization. By modulating this pathway, AFA triggers a controlled release of stem cells into circulation.
Fucoidan works through multiple pathways, including effects on CXCR4 receptors and the SDF-1 signaling axis. These pathways are central to stem cell trafficking and homing to damaged tissues.
The beauty of these natural approaches lies in their selectivity. Unlike pharmaceutical stem cell mobilizers that cause massive, non-specific stem cell release, botanical compounds promote a more measured, targeted response that supports the body's natural healing processes.
Beyond Basic Healing
The applications of endogenous stem cell mobilization extend far beyond basic wound healing. Research suggests potential benefits for:
Cardiovascular health: Mobilized stem cells can support heart tissue repair and blood vessel formation.
Neurological function: Evidence suggests potential benefits for brain health and cognitive function.
Joint and musculoskeletal health: Stem cells may help repair cartilage and reduce inflammation.
Skin regeneration: Increased stem cell circulation may improve skin healing and reduce visible aging.
Immune system modulation: Stem cells play essential roles in balancing immune responses.
Perhaps most intriguing is the potential for these approaches to address the underlying cellular aspects of aging itself. By maintaining higher levels of circulating stem cells throughout life, tissue function and resilience that would otherwise decline may be preserved.
Integrating Stem Cell Mobilization Into Daily Life
The science of stem cell mobilization isn't limited to supplements. Several lifestyle factors significantly influence stem cell function and availability.
Exercise has been shown to trigger acute increases in circulating stem cells. Quality sleep supports stem cell function through multiple pathways, including melatonin production. Stress reduction is equally significant, as chronic stress hormones impair stem cell migration and effectiveness.
Nutritional factors also play a role. Colorful plant foods rich in polyphenols provide antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds that create an optimal environment for stem cell function. Avoiding inflammatory foods and toxins helps prevent stem cell depletion.
Integrating natural stem cell mobilizers with these lifestyle approaches creates a comprehensive strategy for supporting the body's regenerative capacity.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine
As research in this field advances, we're likely to discover additional natural compounds that beneficially influence stem cell behavior. The current focus on AFA and Fucoidan represents just the beginning of our understanding.
What makes this approach particularly promising is its accessibility. Unlike expensive stem cell injections that are out of reach, natural stem cell mobilizers can be incorporated into daily wellness routines.
The implications for preventive health are profound. Rather than waiting for tissues to degenerate to the point of requiring intervention, supporting ongoing stem cell function throughout life may help maintain optimal tissue function and prevent many age-related conditions from developing in the first place.
This shift from reactive treatment to proactive support of the body's natural regenerative capacity represents one of the most exciting frontiers in health science today.
The Bigger Picture
The science of endogenous stem cell mobilization reminds us of something easily forgotten in our technology-focused medical paradigm: the extraordinary healing intelligence built into the human body.
By working with these innate mechanisms rather than bypassing them, we tap into billions of years of evolutionary wisdom. The body knows how to heal itself; sometimes, it just needs the right resources to do so effectively.
This approach doesn't replace conventional medicine but complements it. Traditional interventions remain essential for acute injuries and specific conditions. But supporting the body's stem cell systems offers a powerful additional strategy for ongoing tissue maintenance and addressing the cellular basis of aging.
The hidden healing power of your stem cells may well be one of the most underutilized resources in medicine today. As research continues to validate and refine our understanding of natural stem cell mobilizers, this approach will likely become an increasingly important part of preventive health and regenerative medicine.